分类: 虚拟化技术
RunD – A Lightweight Secure Container Runtime
1. 设计目标
2. 问题分析
2.1 并发启动的开销
2.2 高密部署的瓶颈
kata 系统架构解读
https://github.com/kata-containers/kata-containers/tree/main/docs/design/architecture
https://github.com/kata-containers/kata-containers/tree/main/docs/design
1. 整体架构
如下图:
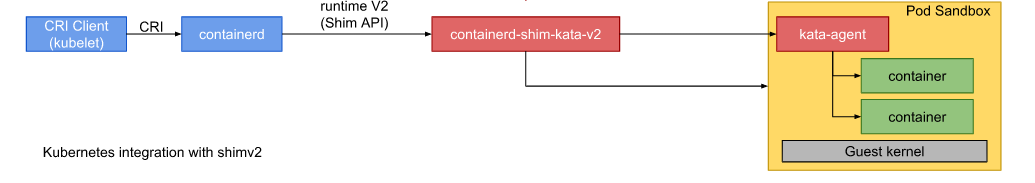
kata-containers 的核心 binary 就2个:
- containerd-shim-kata-v2,对应源代码目录 src/runtime
- kata-agent,对应源码目录 src/agent
containerd 实现了 cri 协议,可以天然直接无缝对接到 kublet 上,而 containerd-shim-kata-v2 实现了 containerd 的 shim-v2 协议,直接实现了对 kata-agent 以及 hypervisor 通讯的封装。
cgroup 内存管理之 tmpfs
1. tmpfs 内存简介
- 首先它是个文件系统
- 但是它的文件数据是完全存放在内存里面的,不在磁盘上
2. tmpfs 文件系统的实现
2.1. virtual file system 接口定义
- 一个是 struct file_operations:文件读写的接口
- 一个是 struct inode_operations:inode操作接口
struct inode_operations {
int (*create) (struct user_namespace *, struct inode *,struct dentry *, umode_t, bool);
int (*symlink) (struct user_namespace *, struct inode *,struct dentry *,const char *);
int (*mkdir) (struct user_namespace *, struct inode *,struct dentry *,umode_t);
int (*rmdir) (struct inode *,struct dentry *);
/* 省略一万字 */
};
cgroup 内存管理之 page cache 回收
- 什么时机会触发 page cache 回收?
- 回收过程是什么样的
- 不可回收的页面有哪些?
- 不容易回收的页面有哪些?
- 回收力度如何控制
1. 整机 drop_caches 回收
- echo 1,清理 page cache
- echo 2,清理 slab,比如 dentry cache 通常也很消耗内存
- echo 3,两种都清理
1.1. 回收时机、力度、算法
1.2. 回收过程
- 遍历所有的超级块,super_block
- 遍历每个超级块上的所有 inode 对象
- 根据 inode->i_mapping 找到每个 inode 的 address_space 空间
- 遍历 address_space 下的所有 page
- 将 page 从 radix tree 上删除
- 调用文件系统的 releasepage 函数释放文件系统资源。这个可以忽略,我看 fs/* 几乎所有文件系统都不实现这个函数了
- 释放所有能释放的 page 内存(引用计数为0)
- drop_caches_sysctl_handler
- iterate_supers(drop_pagecache_sb, NULL)
- drop_pagecache_sb, list_for_each_entry(inode, &sb->s_inodes, i_sb_list)
- invalidate_mapping_pages(inode->i_mapping, 0, -1) // 这个函数的实现在 mm/truncate.c 文件里,Invalidate all the unlocked pages of one inode
- invalidate_inode_page(page) for page in pagevec_lookup_entries(&pvec)
- invalidate_complete_page() 删除page的mapping,并从 page cache 的radix-tree 里面剔除,因为下一步就直接 free 内存了
- invalidate_inode_page(page) for page in pagevec_lookup_entries(&pvec)
- pagevec_release(&pvec) // 释放所有的 page 内存空间
- invalidate_mapping_pages(inode->i_mapping, 0, -1) // 这个函数的实现在 mm/truncate.c 文件里,Invalidate all the unlocked pages of one inode
- drop_pagecache_sb, list_for_each_entry(inode, &sb->s_inodes, i_sb_list)
- iterate_supers(drop_pagecache_sb, NULL)
1.3. 回收范围
- 脏页
- 正在回写的页
- mmap + MAP_SHARED 方式映射到 page table 的页
- PG_SyncReadahead 需要多次drop才能回收
int invalidate_inode_page(struct page *page)
{
struct address_space *mapping = page_mapping(page);
if (!mapping)
return 0;
if (PageDirty(page) || PageWriteback(page))
return 0;
if (page_mapped(page))
return 0;
return invalidate_complete_page(mapping, page);
}
struct address_space *page_mapping(struct page *page)
{
struct address_space *mapping;
page = compound_head(page);
/* This happens if someone calls flush_dcache_page on slab page */
if (unlikely(PageSlab(page)))
return NULL;
if (unlikely(PageSwapCache(page))) {
swp_entry_t entry;
entry.val = page_private(page);
return swap_address_space(entry);
}
mapping = page->mapping;
if ((unsigned long)mapping & PAGE_MAPPING_ANON)
return NULL;
return (void *)((unsigned long)mapping & ~PAGE_MAPPING_FLAGS);
}
cgroup 内存管理之 mlock
1. mlock 的背景
cgroup 进程调度之 Borrowed-virtual-time (BVT) scheduling
1. cfs 睡眠补偿机制
overlayfs 差分文件系统原理
1. upper and lower
2. 用法
docker image 存储剖析
文件系统隔离之 – 深入 prjquota,源码剖析
ext4 prjquota 实现原理,参考了 xfs prjquota,并且复用了linux 内核的磁盘配额管理机制的大部分实现,所以源码上分析起来还是非常简单的
linux内核本身就已经支持user、group级别的磁盘配额管理,用法可以参考:https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/7/html/storage_administration_guide/ch-disk-quotas
从文件系统实现层面来看,文件系统本身并不了解什么是uid,gid,因此disk quota的实现一定是在raw file system 之上的。正因为是如此,所以 prjquota 得以复用原有 disk quota 的大量实现,之需要在原有基础之上,扩展一个新的 quota 类型而已
具体内核提交的 patch:https://lore.kernel.org/patchwork/patch/541891/
4.14 内核时,已经进入主干,因此可以参考:https://lxr.missinglinkelectronics.com/linux+v4.14/fs/ext4/
简述一下其基本设计:
- 在 super block 中,有一块专门用来存储 project id 用量的元数据区
- 每个文件,属于哪个 project id,是记录在文件的 xattr 属性里面的(正是因为 ext4 文件系统支持 xattr 扩展,所以才很方便的移植这个特性)
- 文件写入的时候,先查找这个文件的 project id,然后判断当前 project 的 usage + 文件的增量的大小,是否超过 project 的 hardlimit,如果超过,返回 EDOUT,文件写入失败